How to Get Rid of White Fuzzy Mold on Plants [Powdery Mildew]
White fuzzy molds grow on plants when fungal spores germinate. Also known as mycelium, the white fungi appear on plants that are underexposed to sunlight.
Other causes of molds include overwatering in poor lighting conditions. The fuzzy molds appearing on plants symbolize an infection that may pose danger to a plant.
What’s the White Stuff on Plants?
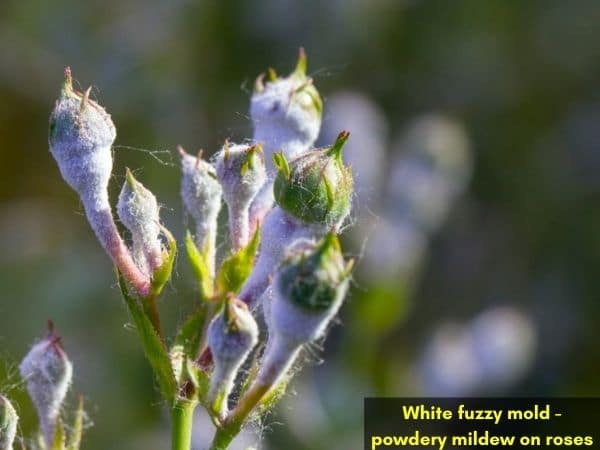

The white stuff appearing on plants is powdery mildew. It is a fungus that appears as a white or gray substance that spreads on flowers, fruits, and buds of a plant.
The white stuff grows in form of fungus spores and quickly spreads into a white fuzz that’s commonly referred to as powdery mildew. Powdery mildew fuzz commonly affects plants that are exposed to warm, humid, or damp growing conditions.
How To Get Rid of White fuzzy Mold on Plants
Here’s how to get rid of the white fuzzy mold on your plants:
Milk
The use of milk has proved to be effective in getting rid of fuzzy molds on plants. Though not scientifically proven, the compounds available in milk not only help improve the immunity of a plant but also act as a fungicide. It is one of the effective ways to get rid of mildew on cucumbers, zucchini and various types of squash.
Here’s how to use milk to get rid of the white fuzz on plants:
- Mix one part to three parts of water
- Sprinkle overhead to the entire plant
Baking Soda
Baking soda is a great fungicide that’s found in almost every household. A combination of baking soda, water, and liquid soap has proven to be effective in treating mildew. In normal circumstances, it is used to prevent the growth of molds than treatment.
- A half teaspoonful of liquid, a gallon of water, and detergent-free soap mixed can be used to spray the plants.
- Mix proportionally then sprinkle on the plant overhead.
Use fungicides
If other alternatives aren’t giving desired results, fungicides come in handy to offer an ultimate solution. Environmental friendly fungicides are available in the market that can be purchased for use in spraying plants.
Before opting for this route, it’s important to note the most appropriate chemical needed for the task. This saves from the danger of spraying wrong fungicides that may endanger plants.
Water
High humid and dry environmental conditions are a recipe for mildew. In that case, an overhead spray of water can be effective in getting rid of the fuzzy molds. On the flip side, this type of method should be used sparingly since overwatering can have other adverse effects on plants.
- Fetch water and sprinkle on the plant from overhead
- Ensure you don’t over sprinkle since too much water may also affect the plant
Mouthwash
Did you know that the mouthwash used daily can be effective in getting rid of molds on your plants? The germ-killing substances in toothpaste can help get rid of fungus on plants. Since the role of mouth wash is to kill germs, fungi spores also die when they come into contact with mouthwash.
Though the method works, great caution is required to avoid any possible side effects of mouthwash on plants.
To use mouthwash to get rid of white fuzz on plants, mix three parts water with one part mouth wash and apply it on the affected plants. The ratio is effective since an imbalance may affect your plants.
Can Mold Grow on Roots?
Molds are fungus that can grow on any part of a plant that is subjected to low light conditions. The growth of molds on soil can cause root rot that can kill the plant if not treated on time. One of the major causes of root rot is overwatering indoor plants like peace lilies, cactus, pothos, and more.
The exposure of roots to gray mold spores results in unhealthy, mushy, discolored roots. Stems and leaves can also start to discolor and become weak due to the failure of nutrients to move up and down the plant.
How to Prevent Root Rot in Plants
If you’re repotting the plant that’s suffering from powdery mildew or white fuzz, there’s quite a few things you can do to prevent the plant from getting root rot. Here are some of the tips to consider:
- Drying out the potting soil in the sun before repotting
- Get rid of molds from the plant and spray with fungicides on the stems and leaves
- Apply an anti-fungal to the soil
- Repot new plants into sterile soil or a new potting mix that’s not expired.
Symptoms of Plant Molds
Symptoms of mold are usually visible on various parts of a plant. If you expose your plant to less light and high humid environment, then you are likely to observe the following features on your plant.
The powdery deposits appear on buds, leaves or shoots of a plant and can make the entire shoot white dirty. Though the mildew is unlikely to kill the plant, it weakens and damages the roses. The following are other symptoms of fuzzy mold attacks.
- Wilting of leaves
- Rotting of pods
- Leaves turning to yellow
- Gray mold. This is a fungal disease that attacks the whole plant
- White powder appearing on the leaves
- The appearance of water-soaked spots on leaves.
Commonly Affected Plants
The effects of powdery mildew are mostly common on green parts of pea plants. The disease is common in Ornamentals, Vegetables, most flowers and woody plants.
Greenhouse crops susceptible to powdery mildew include the following.
- African Violet
- Dahlia
- Hydrangea
- Roses
- Verbena
- Poinsettia
- Gerbera daisy
- Kalanchoe
Ways To Prevent Powdery Mildew on Plants
- Chose plants that are powdery mildew resistant. Such varieties include cucurbits (cucumbers, Squash, melons etc.) These varieties can easily be bought from seed suppliers.
- Plant where the sun is likely to hit your plants well because powdery mildew develops in shady areas.
- Always water from the overhead to wash spores away from the leaves.
- Increase air circulation through pruning bushy plants such as peace lilies. Pruning helps reduce humidity to discourage the growth of powdery mildew.
- Spray infected plants with fungicides
In case you want to avoid using chemicals in your small garden, you can opt for a bicarbonate solution as a homemade control for white stuff on plants.
To control the spread to other plants, get rid of all infected stems, foliage, fruits, or any other parts by destroying them. You can either through away the pruned parts or burn them.
When seedlings are affected by damping off, plants fail to develop a strong stem. As a result, the fungi affect the stem, rooms and prevent the movement of nutrients in various parts of a plant.
Growers need to put their plants in check to oversee any signs of mold to save a plant before serious damage is observed. While small plants affected by molds may recover, mature plants may hardly survive the effects of fungi.