How to Get Rid of Mistletoe in Trees
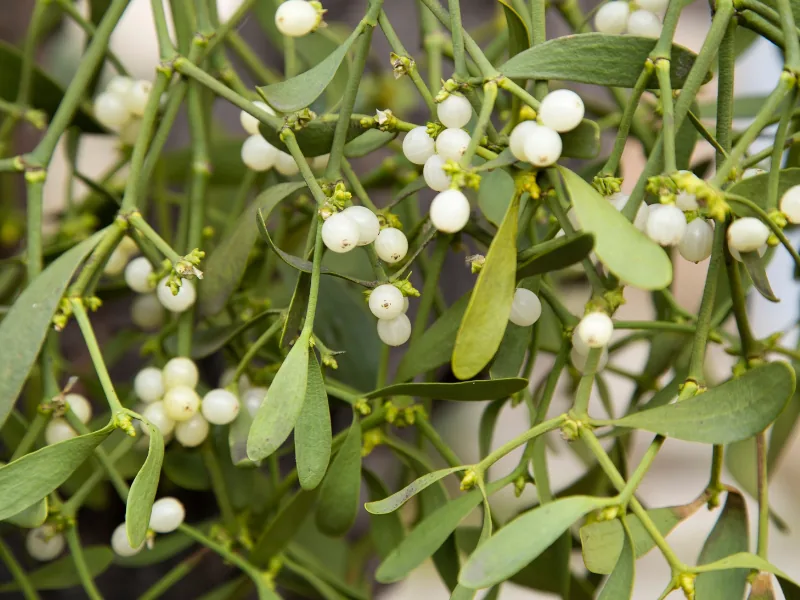

Mistletoe is a hemiparasitic plant that depends on its host tree for nutrients even though it carries out photosynthesis. Severe infestation can easily kill the host plant within 10 to 15 years, so it is important to get mistletoe out of trees early enough.
Most trees can resist mistletoe infestation, but the pest can reduce the yield of your fruit trees incrementally over the years.
How to get rid of mistletoe
Here are the effective ways to control mistletoe in trees:
Pruning
Mechanical removal of mistletoe is the most effective way to control the established pest. Cut the mistletoe back at the branch collar to prevent it from growing to seed.
In most cases, pruning is only necessary if the infestation is heavy and the mistletoe exerts too much stress on the host plant.
Here’s how to prune mistletoe out of trees:
- Cut off the affected tree branches as soon as you notice mistletoe growing to prevent it from spreading.
- Cut back to the branch collar or to a secondary branch to help the tree recover from the removal.
- Ensure you cut 10-14 inches from the mistletoe’s point of attachment since the haustoria grow deep within the host’s branches.
- If the mistletoe grows less than 10 inches from the trunk or primary branch, cut off the branch.
- Cover the pruning wound with a black plastic bag to cut off sunlight and prevent mistletoe from growing.
It is vital not to over-prune your tree. In young, healthy plants, do not prune more than 20 to 30%. For mature or unhealthy plants, do not prune more than 10% yearly.
Chemical treatment
Using growth-regulating hormones is also an effective way to get rid of mistletoe. This method is temporary when the mistletoe is well established.
Spray a plant growth regulator like Ethephon on mistletoes to dry out flowers and shoots and force them to fall off the tree.
Here’s how to apply Ethephon to kill mistletoe:
- Mix ¼ to ½ part of Ethephon with two gallons of water.
- Spray the mixture on mistletoe, ensuring the leaves are wet.
- Ethephon takes 7-14 days to work. Therefore spray on mistletoes early enough before they go to seed.
- Repeat the treatment every 3-4 years to kill new mistletoe growths from haustoria.
Pro tip: Treat mistletoe when the host plant is dormant to avoid killing it.
While this method is effective in orchards, the mistletoe’s root system (haustoria) remains beneath the bark and leads to regrowth.
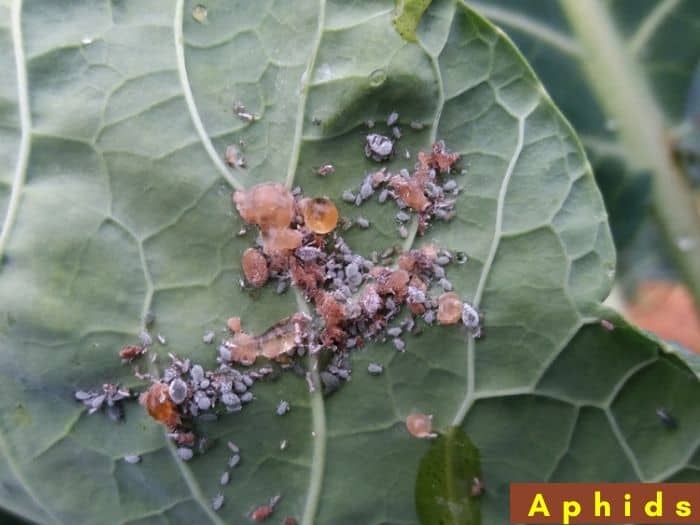
Biological control
Biological control using insects such as aphids to feed on the mistletoe’s sap, leaves, shoots, flowers, and fruits is also said to be effective for dwarf mistletoe varieties.
A heavy infestation of insects on the mistletoe weakens it, leading to its death. However, this method is less effective than chemical and mechanical control.
Planting resistant species
You can prevent mistletoe by planting tree species that are resistant to the parasite. Some of these trees include eucalyptus, sycamore, Bradford flowering pear, conifers such as cedar and redwood, golden-run tree, and the Chinese Pistache tree.
On what trees does mistletoe grow?
Mistletoes grow on branches of large deciduous trees like pine and oaks. Some mistletoes prefer orchard fruit trees such as apple, lime, and guava trees.
Mistletoes prefer hosts in open fields with plenty of natural light. That is why mistletoes do not grow in woodlands.
Different species of mistletoe prefer different types of host plants. Below are some of the plants that mistletoes prefer:
- Pine trees: The fruitless dwarf mistletoes (Arceuthobium species) infest pine trees and other conifer species. Common varieties that affect pines include Lodgepole pine dwarf mistletoe, Pinyon dwarf mistletoe, Southwest dwarf mistletoe, Limber pine dwarf mistletoe, and Douglas-fir dwarf mistletoe.
- Oak trees: The American mistletoe, also known as the oak mistletoe (Phoradendron serotinum), usually infests deciduous trees, including the oak group.
- Guava fruit tree: Mistletoes of the genus Tapinanthus (Loranthaceae and globiferus) are stem hemiparasites with colorful red flowers. The Tapinanthus genus mistletoes prefer the orchard fruit plants, such as guavas.
Can mistletoe kill trees?
Yes. Severe mistletoe infestation can kill trees by extracting water and nutrients from the healthy hosts and weakening them.
However, the parasite grows slowly and does not pose an immediate threat to healthy plants. So, healthy plants can tolerate a few mistletoes with little harmful effects.
Heavy infestation causes stunted growth, dead branches, and swelling on branches, thus subjecting the infected host plant to more stressful conditions like drought, pests, and diseases.
References
- Colorado State University, Extension: Methods to control mistletoe 199129111.pdf
- S. F. Shamoun, L .E. DeWald: Management Strategies for Dwarf Mistletoes



![How to Get Rid of White Fuzzy Mold on Plants [Powdery Mildew]](https://gardenine.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/04/White-fuzzy-mold-on-plants-powdery-mildew.jpg)